Hearing a lot of ‘proxies’ everywhere? People often confuse proxy servers with VPNs, and there’s not much clarity. Proxies are being widely used for various security reasons, such as concealing one’s identity or footprints from cyberspace. This article comprehensively talks about a proxy server, types of proxies, understanding the use cases of proxies, setting up a proxy server, and pros and cons.
Without wasting any more time, let’s dive in to know more.
Understanding a Proxy Server
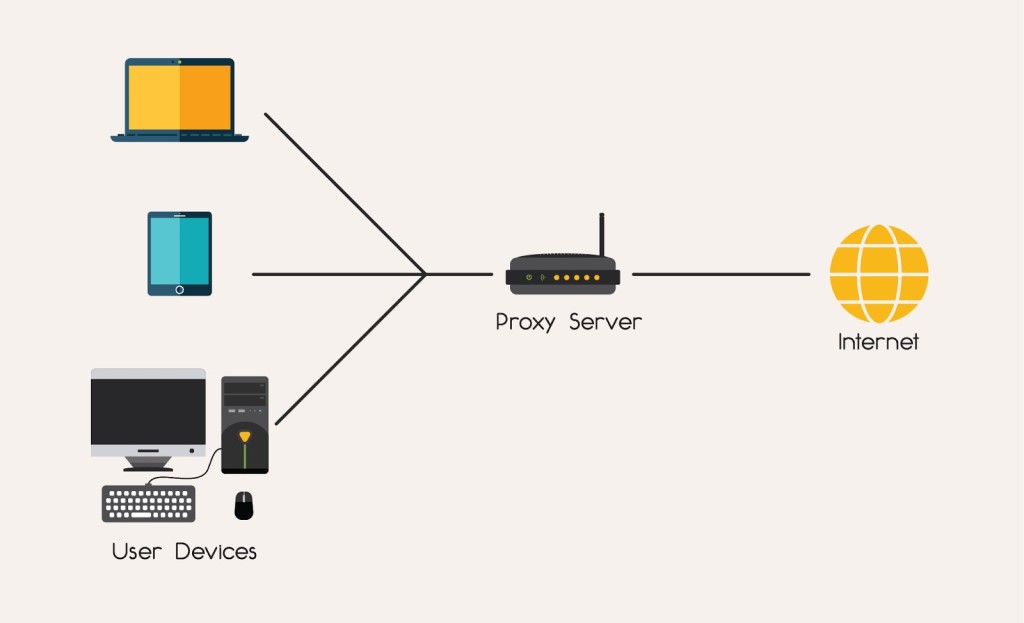
To explain in simple terms, a proxy is someone who does a task on your behalf for others. Proxy is that system that sits intermediate between the organization and the internet. Other definitions include specifying a proxy as a bridge connecting your digital assets with the infrastructure so that all requests pass through the proxy.
Imagine a scenario where a device with proxy settings requests information from a website. This website receives and delivers concerning information to the proxy. The internet will never know the accurate details, such as the device’s IP.
Use cases of proxies
Various users often opt for proxies for their remarkable feature of geo-bypass to access and surf restricted content. Additionally, people with bandwidth issues can make use of proxies.
These use cases mentioned above apply to businesses as well. Various organizations use proxies to gain insights into search engine optimization and data crawling. For social media monitoring and data collection, proxies are extensively being utilized. Companies also investigate ad fraud, given the security advantages of proxies.
Companies with significant human resources often face a considerable burden on the stability of the servers. Proxies rightly step in here and offer better load balancing and stabilization of the servers.
Types of proxies
Many people know only a handful of proxies and their settings. However, we have a lot more than that. Let’s summarize the types of proxies we know in short.
Open Proxy
An open proxy is as simple as connecting to public WiFi. There’s no provision for security or anonymity with an open proxy.Reverse Proxy
A reverse proxy, as it is known, sits in the back-end directing requests from the clients to the appropriate servers. It comes with maximum performance benefits and a secure environment from web-based attacks.Anonymous Proxy
An anonymous proxy conceals your digital footprints on the internet and makes them untraceable. It hides the original IP of the device and acts as a relay with the websites it interacts with.Transparent Proxy
A transparent proxy, also called an inline proxy, provides efficient performance with limited bandwidth. It doesn’t mask your IP and doesn’t need any client-side configuration. The purpose is to improve efficiency with the help of caching.CGI Proxy
CGI stands for common gateway interface. It enables a website form that users can access to surf anonymously and connect to the internet.Suffix Proxy
As the word suggests, when connected to a suffix type of proxy, it suffixes a name at the end of the URL and then displays the requested website.
Setting up a proxy server
Setting up a proxy server has been made easy with Windows. To set up a proxy server with Windows, simply visit ‘Settings’ and select ‘Network and Internet’. You might see an option of Proxy and set up a manual proxy as per needs.
Besides that, there are different third-party proxy servers and completely affordable services one can use.
Pros and cons of a proxy server
Proxy servers protect your identity (IP address) on the internet by acting as a proxy for your digital footprints. Like a VPN, a proxy will overcome geographically restricted access and present that content to you, with some decent filtering options from harmful websites that try infecting the user’s device.
Thus, malware, adware, spyware, and trojans can be evaded from attacking your assets sitting behind the proxy. Compared to other anonymity providers, proxies can be lighter on pockets and an ideal choice for someone who enjoys privacy but is not overly concerned about it.
Organizations can also use proxies to compress traffic and monitor the activity of their employees as administrators.
However, there are certain things that we need to be cautious about while using proxy servers. Certain third-party proxy providers might have vulnerabilities that can let attackers exploit or have access to your devices.
Sometimes there’s redundancy in the performance of proxies, and VPNs do not operate alongside.
One of the most significant disadvantages of proxies is that they might store and sell your browsing patterns and saved data to potential buyers. Thus, your privacy might be safeguarded from the internet, but not from the vendors interested in buying it.
Towards the conclusion
As we conclude in this article on understanding a proxy server, we hope a slight idea of proxies, their types, and who it is made for is clear. To annotate the use cases of proxies, it has been heavily used for SEO and scraping, besides providing anonymity and stability to the server. If you are considering using a proxy, look into this article and make the best choice.

Author Bio: This article has been written by Rishika Desai, B.Tech Computer Engineering graduate with 9.57 CGPA from Vishwakarma Institute of Information Technology (VIIT), Pune. Currently works as Threat Intelligence Researcher in CloudSEK. She is a good dancer, poet and a writer. Animal love engulfs her heart and content writing comprises her present. You can follow Rishika on Twitter at @ich_rish99.