Network attacks and online risks are propelled each hour consistently, and they advance at a fast pace. Hackers keep bringing new threats and attacks. Numerous individuals depend on the Internet for their social, personal and professional activities. There are also individuals who endeavor to harm our Internet connections, destroy our software, abuse our protection and invade our privacy.

Given the recurrence and variations of existing attacks and the danger of new and increasingly harsher future attacks, network attacks and security has turned into a focal subject in Computer Networking. The following are the most common types of network attacks.
1. Malware Attack

In the event you might have seen an antivirus alert spring up on your screen, or that you erroneously clicked on a malicious link, at that point you had a narrow escape with malware. Security attackers enjoy getting a hold of the user’s system through malware. If a PC in the office has been attacked, the online system as a whole of the organization is under attack. “Malware” means different types of evil and dangerous programming, for example, ransomware and viruses. If malware has entered your PC, then it can unleash a wide range of destructive programming such as controlling your device, checking your activities and keystrokes, sharing confidential information from your cloud or disk to the attacker’s command post. Attackers will utilize an assortment of strategies to send malware in your device. However in most cases, it requires the client to make a move to introduce the malware; such actions include opening a random attachment, clicking on a link to download something, etc. The best way to stay safe from malware is retraining from clicking random links and opening spam messages and suspicious email attachments.
2. Denial-of-Service Attack
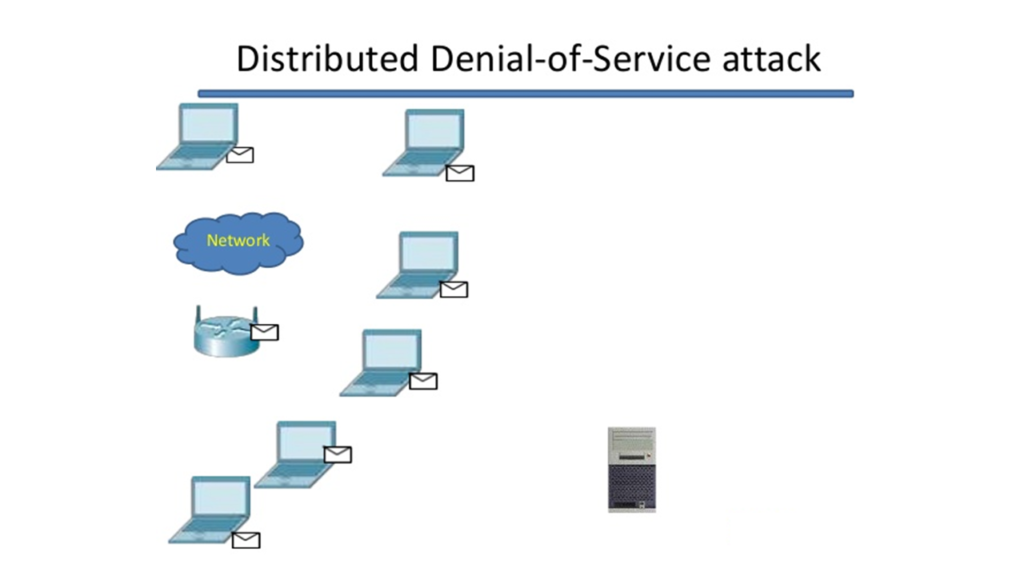
The denial-of-service attack averts typical utilization of your PC or network by regular clients and users which is not the same as password attack. The denial-of-service attack gives the attacker the access to block the traffic, share invalid information with networks and applications, cause unexpected behavior and changes in programs, flood the whole network or your device with traffic, an over-burden of coding to cause shutdown, diversions for more attacks and to randomize the user interface, so the system security is not warned. You can stay safe from this attack by regularly running antivirus software and system scans on your PC.
3. Application-Layer Attack
This attack aims to target the application servers and causes a glitch in the operating system of software of the server. The hacker picks up the capacity to sidestep universal access controls and exploits the information in the system. He can easily access your applications, framework or network which enables the attacker to:
- Dissect your network and acquire personal data
- Crash or corrupt system and network
- Read, erase, change add data in your operating system
- Use your PCs programming to duplicate and spread virus all through your network
- Host a virus program into your device
- Abnormally dismiss your programs
- Disable security controls
4. Packet Sniffer
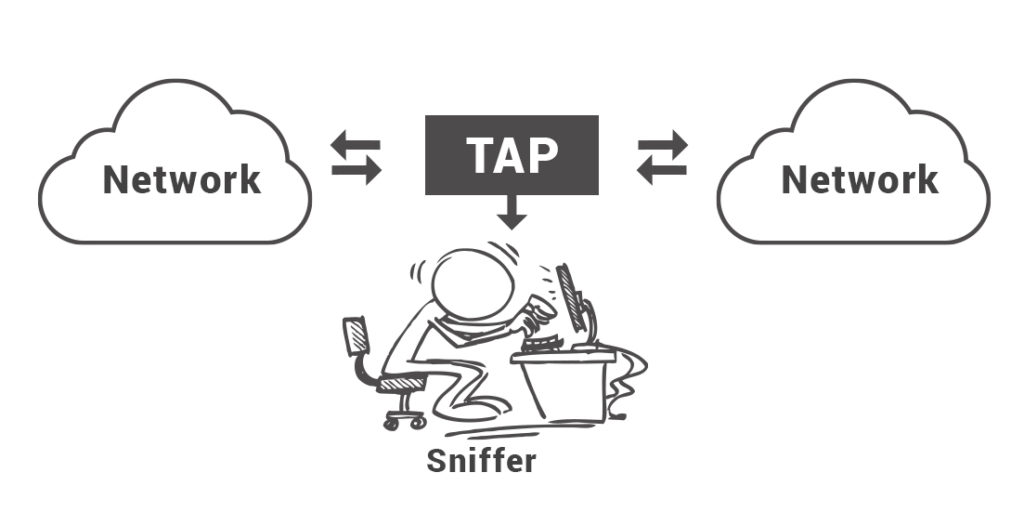
A packet sniffer is a hidden recipient which maintain and records a duplicate copy of each packet flying through the network. The hacker places a passive recipient in the region of the remote transmitter and gets a duplicate of each packet being transmitted over the network. People can gain access to all type of sensitive information via packet sniffers. These include passwords, account numbers, trade secrets, social security numbers, confidential files, and personal images. The best way to stay safe and guard against this type of online theft is by using cryptography to encode every message you send on the network. According to the IT Head of ClothingRIC, you can stay safe from network attacks by:
“Don’t click on a link right away; take your time to assess the validity of it. Place your mouse over the link and check that the link matches the URL.”
5. Man-in-the-Middle Attack
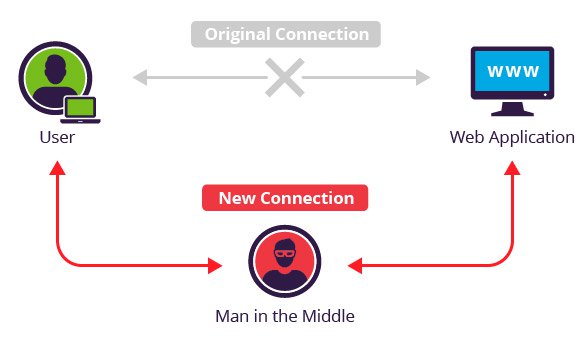
Pretty evident from the name, a “man in the middle” attack happens when there is a third party present between you and the other party you are communicating with. This enables the hacker to effectively observe, catch, control and steal the information being shared between the two parties. PCs with low network layers can be easily at attack by using this technique. Hence, the simplest way to stay safe from man-in-the-middle attack is by having a secure and robust network protection layers.
You’ll also like to read: Protection From Common Network Attacks (Part 2)